Representation¶
CSKG is modeled as a hyper-relational graph. It describes edges in a tabular format, following the KGTK data model and file specification.
CSKG columns¶
The edges in CSKG are described by ten columns, which can be grouped into three groups:
* Following KGTK, the primary information about an edge consists of its id, node1, relation, and node2 (default edge columns).
* Next, we include four lifted edge columns, using KGTK's abbreviated way of representing triples about the primary elements, such as node1;label or relation;label (label of node1 and of relation).
* Each edge is completed by two qualifiers (secondary edges): source, which specifies the source(s) of the edge (e.g., "CN" for ConceptNet), and sentence, containing the linguistic lexicalization of a triple, if given by the original source.
Summarizing, here are the 10 columns that comprise the CSKG edge representation:
idis an edge identifier, constructed by concatenating its node1, relation, and node2 elements. We aim to have edge ids be consistent across CSKG versions.node1is a node identifier, must have a single value, cannot be empty, cannot have empty spaces.relationis an identifier, must have a single value from a predefined list, cannot be empty, cannot have empty spaces.node2is a node identifier, must have a single value, cannot be empty, cannot have empty spaces.node1;labelis a textual label fornode1. It can have multiple different values, separated with a "|" character. Can be empty.node2;labelis a textual label fornode2. It can have multiple different values, separated with a "|" character. Can be empty.relation;labelis a textual label forrelation. It can have multiple different values, separated with a "|" character. Can be empty.relation;dimensionis an abstract knowledge type for a relation (e.g., "spatial"), one of the predefined 13 categories in this paper. Can have multiple values. Can be empty.sourceis a list of the source KGs in which this edge was found (e.g., ConceptNet). Can have multiple values, separated by "|". Can be empty.sentenceis the original sentence from which the triple was derived. Can have multiple values, separated by "|" (in case we have multiple sources). Can be empty.
Example¶
Let's start with a simplified Figure of CSKG that talks about playing piano:
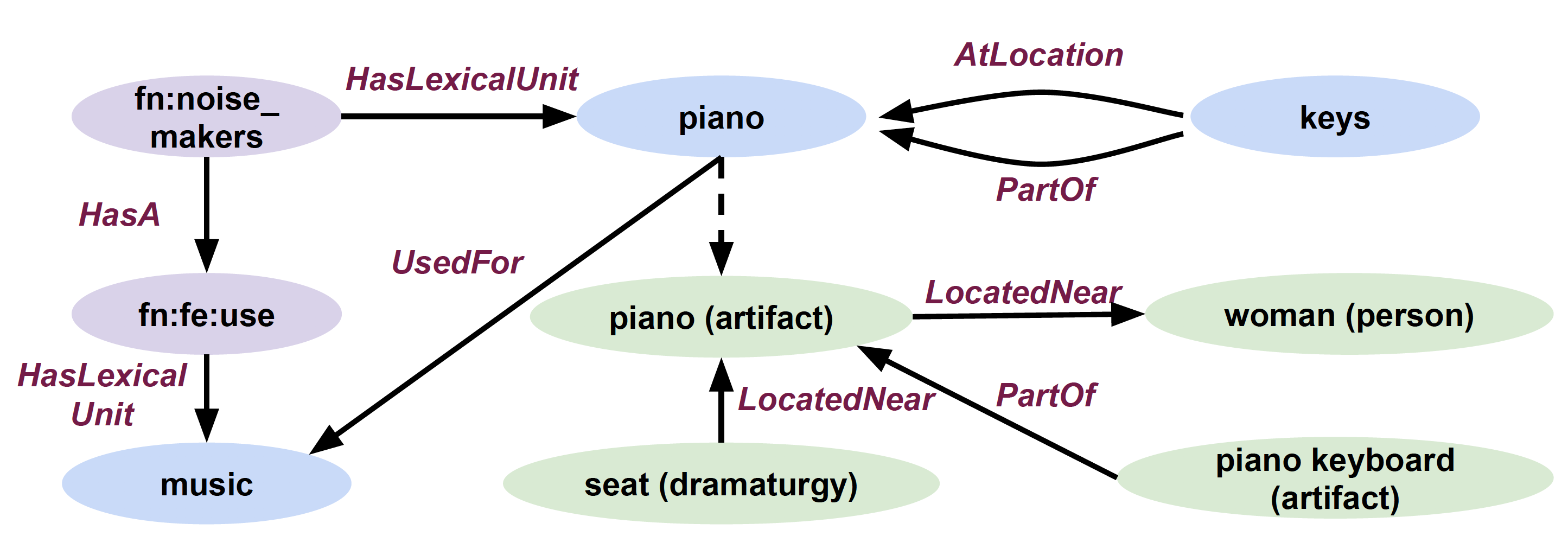
Here are the set of edges in CSKG that correspond to the Figure:
| id | node1 | relation | node2 | node1;label | node2;label | relation;label | relation;dimension | source | sentence |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| fn:noise_makers-/r/HasA-fn:fe:use-0000 | fn:noise_makers | /r/HasA | fn:fe:use | noise makers | use | /r/has a | part-whole | FN | |
| fn:noise_makers-fn:HasLexicalUnit-fn:lu:noise_makers:piano-0000 | fn:noise_makers | fn:HasLexicalUnit | fn:lu:noise_makers:piano | noise makers | piano | has lexical unit | lexical | FN | |
| fn:fe:use-fn:HasLexicalUnit-/c/en/music | fn:fe:use | fn:HasLexicalUnit | /c/en/music | lexical | FNC | ||||
| /c/en/piano-/r/UsedFor-/c/en/music-0000 | /c/en/piano | /r/UsedFor | /c/en/music | piano | music | used for | utility | CN | [[a piano]] is for [[music]] |
| /c/en/keys-/r/AtLocation-/c/en/piano-0000 | /c/en/keys | /r/AtLocation | /c/en/piano | keys | piano | at location | spatial | CN | *Something you find on [[a piano]] is [[keys]] |
| /c/en/piano_keyboard/n/wn/artifact-/r/PartOf-/c/en/clavier/n/wn/artifact-0000 | /c/en/piano_keyboard/n/wn/artifact | /r/PartOf | /c/en/clavier/n/wn/artifact | clavier|fingerboard|piano keyboard | forte-piano|piano|pianoforte | is a part of|part of | part-whole | CN|WN | [[piano keyboard]] is a part of [[piano]] |
| /c/en/clavier/n/wn/artifact-/r/LocatedNear-/c/en/woman/n/wn/person-0000 | /c/en/clavier/n/wn/artifact | /r/LocatedNear | /c/en/woman/n/wn/person | piano | woman | near | spatial | VG | |
| /c/en/seat/n/wn/dramaturgy-/r/LocatedNear-/c/en/clavier/n/wn/artifact-0000 | /c/en/seat/n/wn/dramaturgy | /r/LocatedNear | /c/en/clavier/n/wn/artifact | seat | piano | for | spatial | VG |
The first two edges, stating that pianos can be noise makers and that noise makers have a use, are from FrameNet (FN). The third edge, stating that this use is for music comes from our FNC mapping between FrameNet and ConceptNet. ConceptNet (CN) itself tells us that keys are parts of a piano, located at a piano, and that pianos are used for music. Next, WordNet and ConceptNet (CN|WN) tell us that piano keyboards are parts of pianos. Finally, Visual Genome (VG) informs us that seats may be located near pianos and pianos near women.
Auxiliary files¶
CSKG is mainly described with a single tabular file. Auxiliary KGTK files can be added to describe additional knowledge about some edges, such as their weight, through the corresponding edge ids.